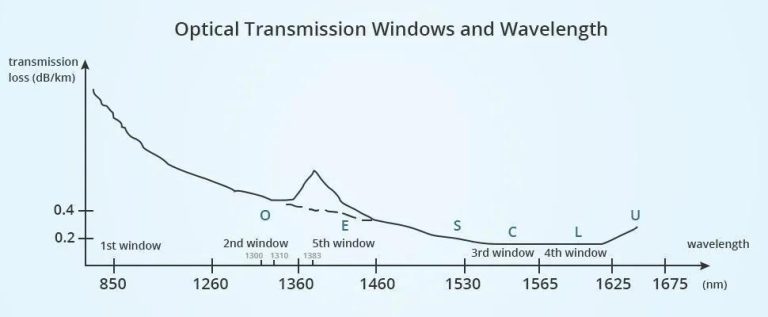
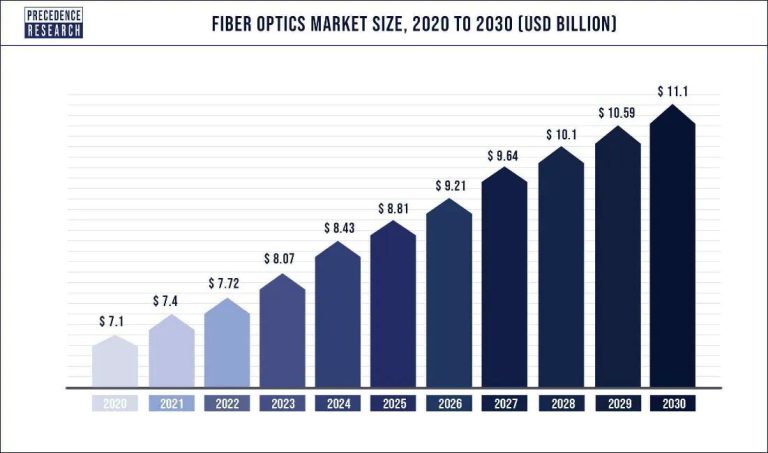
What You Must Know About Optical Fiber Cable: Types and Installation Tips
Augmenting the presence of optical fiber has become a high priority for several countries across the globe. The need to understand how these cables have suddenly gained popularity is important. These elastic cables will end up disrupting technologies in ways beyond our belief. Ever since the internet became a must-have in many households, optical fiber cables have become the latest buzzword. With a continuous push for higher bandwidth, technologies like cloud computing and web services have pushed data limits to new heights.
Optical Fiber Cables – Some Interesting Facts
We know these shiny new cables bring tremendous power and speed. They are predominantly made of glass, silica, and plastic. They ensure minimal data loss when light signals traverse through these cables. The traditional copper wire had a poor information transfer speed and accounted for a higher data loss. However, the optical fiber cable overcomes this and reduces operational support and installation costs.
Though theprice of optical fiber might be comparatively higher, when you think long term, the maintenance costs are comparatively low, and overall, it provides a better proposition. In addition, other benefits like improved security, superior network speeds, the ability to run over long distances, minimal signal interference, and ease of installation ensure that you are never left behind in the race.
Types of Optical Fiber Cables
Optical fiber cables can be classified based on how light propagates, the material used, and the refractive index. Some of the different types of optical fiber cables include:
- Step index optical fiber – Here, the refractive index is the same across both the center of the core as well as at the extremes. The light travel is slightly uncontrolled, but all the light rays will eventually travel at the same speed.
- Graded index optical fiber – In the case of refractive index, we see a lot of variation from the center of the core to what it is at the extremes near the cladding. In the center, light travels slowest, as the refractive index over here is the highest compared to the other areas. However, the optical fiber price for the graded variant is on a slightly larger scale than the step variant.
- Plastic optical fiber – This is an acrylic or polycarbonate core with a resin cladding that is typically made with silicone. They do have the ability to withstand environments that have a lot of vibrations and are more flexible and bendable in comparison to glass optical fibers. However, it does not suit harsh environments and degrades over time. It is mainly used in decorative and illumination appliances. It is also used in medical instruments where a narrow spectrum of light needs to be transmitted.
- Glass optical fiber – Glass core with a glass or plastic cladding is the most common type of optical fiber cable. A large numerical aperture allows a lot of light to traverse in this variant. The ability to withstand extremities in temperature and a corrosive environment comes in favor of this type while making a choice. The overall loss applicable to this variant is lesser compared to other variants. However, this is unfortunately prone to breakage unless handled with care. Sensors and measurement systems typically opt for a glass optical fiber.
- Single Mode fiber – The single mode fiber is a winner when it comes to the transmission distance. It is used for both short-distance and long-distance scenarios. These have a small core size, allowing just a single mode of light to penetrate them. The presence of a large core makes it easier to capture the ray of light from any transceiver.
- Multi-mode fiber – It is a cost-effective alternative compared to single-mode optical fiber. Also, with regards to installation, multi-mode optical fiber is easier to install when compared to other types.
Installation Tips
Fiber cables can be deployed both aerially and underground. The aerial optical fiber cable can be efficient to deploy, but we need to understand the circumstances and environment before making a choice. Some important tips that would come in handy include:
- Use an automated puller when possible. This ensures we never exceed the benchmark pulling ratings.
- A fiber optic cable generally has a rod made of fiberglass to provide additional strength. So care is required that you do not end up pulling the fiber directly.
- Never end up spinning off the cable from the spool end. Instead, always ensure that you gently roll off the cable from the spool.
- Take care to understand the cable bend radius. A tight bending can cause more harm or even breaks and render the cable useless.
- Cables can be put inside an inner duct when you are running them inside your home, office, or factory. The chances of accidental cutting of cables in indoor facilities are common, and it makes sense to use an inner duct as an identification.
- Always try to make the entire fiber line in a single pull. If you end up splicing, the implications include higher costs and maintenance overheads.
- Planning an installation on paper is an absolute must. This eliminates 95% of the problem.
- Pushing a cable can impact the bend radius. Always one needs to pull at the cable during installation.
- Careful monitoring of the supply reel ensures that the minimum bend radius applicable to you never ends up being violated.
- One needs to monitor the installation path carefully and ensure proper communication to avoid the cable jumping of pulleys that miss proper monitoring from the staff.
- When there is a need to install in conduits, always ensure to lubricate the cable to avoid breakage
- The installation quality may not be remarkable unless the correct tools and techniques are in place. The technique of laying a cable in a tray could be one such example for this case.
- Cable design and the installation location are paramount to the success of the installation.
- Always divide the long pulls into shorter ones to prevent the cable from getting twisted.
- When installing cables in vertical installations, it is necessary to understand the vertical rise limits.
- The temperature range in the installation site needs to be studied. Improper temperature fluctuations can cause relatively high attenuation.
- Avoid vehicles from driving over fiber cables that are placed in open areas.
- Having a slack cable of around thirty feet in length can come in handy in case of a cable relocation or repair.

Conclusion
Optical fiber’s proliferation will shoot up rapidly with the evolution of 5G in developing countries. It is important to understand and choose the right type of optical fiber that suits the need and the use it is going to be subjected to. The careful installation will help improve the optical fiber expectancy and enhance the overall transmission rates.